Startup activities begin with risk assessment and safety planning for each phase of the construction, once the workpoint and work and storage areas are determined on the SUP.
Construction Health and Safety Plan
Skilled managers anticipate potential hazards by assessing risks for each phase of the construction. A safety plan is then drawn to identify challenging actions during the construction process, utility locations, potential hazards, environmental impact, and the location of field tests to determine soil conditions.
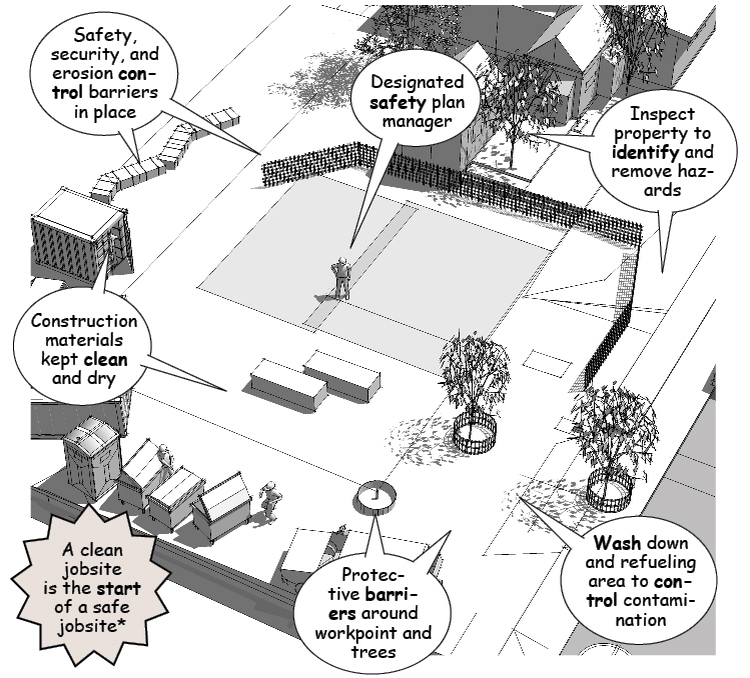
On a large project, a safety plan manager is appointed to continually review operational risks, maintain safe practices, assess environmental impacts, and keep everyone on the jobsite aware of the importance of regulating health and safety.

Written safety plans are usually required by construction insurance carriers and are important to document pre-emptive planning in the event of an injury, subsequent law suit, and worker’s comp claims against the contractor and owners.
Startup Utilities for the Construction
Once setbacks and work areas have been generally identified, utilities are located and marked for connection. Power is needed immediately to construct formwork and falsework to reinforce existing structures. Water is necessary to keep workers hydrated, dust control, and equipment wash-off.

Special concerns include overhead power lines, underground utilities, soil contamination and containment, water and erosion, and natural drainage patterns during construction.

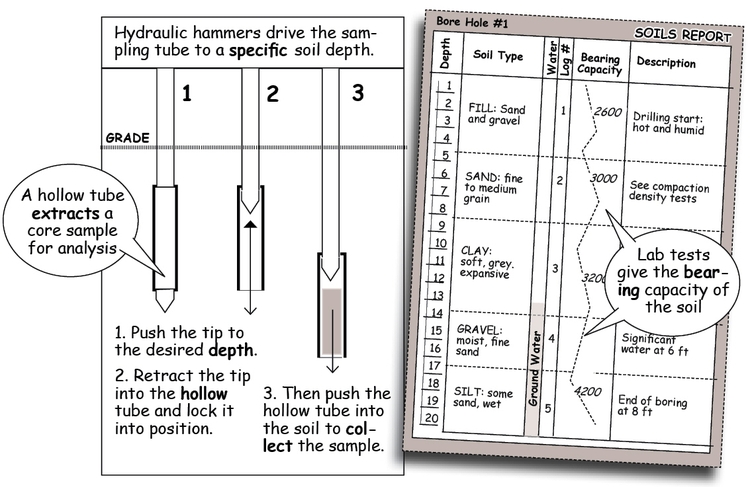
Field Testing
Soil tests determine bearing capacity and moisture content. Tests look for clay that could push up on the foundation and utility lines, as well as sandy soils that could shift or sink under the weight of backfill or the building.
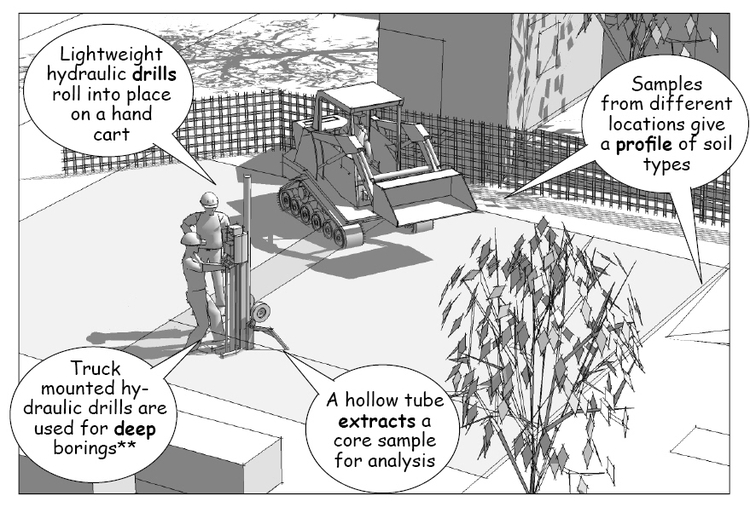
These tests are important to construction planning because they disclose potential problems not only with the foundation for the building, but for slump and sluff factors that may require shoring for utility trenches and the walls of the building excavation.
(To be continued…)

---------------------------
The material presented in this series has been taken from our book, “How a House is Built: With 3D Construction Models” The book includes annotated illustrations, captioned text, videos, models, and the 2D Preliminaries.

